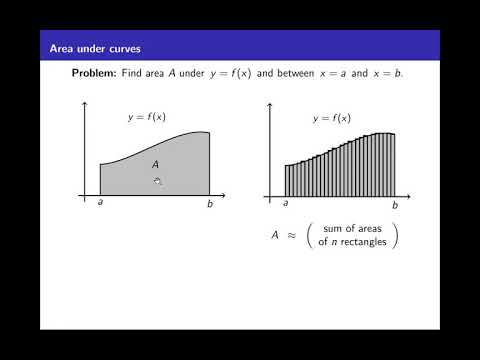
If f(x) = 5x^(2)−6x, 0≤x≤3, evaluate the Riemann sum with n=6, sample points to be right endpoints.

Riemann Sum for Right End Points Example n=6 and a=0 and b=3Подробнее

If f(x) = 5x^2 - 4x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 3, evaluate the Riemann sum with n = 6, taking the sample points t…Подробнее

Riemann Sums - Left Endpoints and Right EndpointsПодробнее

Practice Exam 4 - Calc 1 - 5.2.22 (Evaluating definite integral by Riemann Sum method)Подробнее
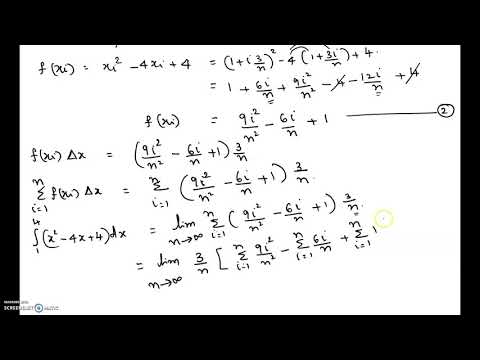
If f(x) = 3x^2 - 4x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 3, evaluate the Riemann sum with n = 6, taking the sample points t…Подробнее

Evaluate the riemann sum with n=6, taking the sample points to be left endpoints. (Give you answer)Подробнее

If f(x) = 4x2 9x, 0 x 3, evaluate the Riemann sum with n = 6, taking the sample points to be ri…Подробнее

Evaluate the Riemann sum for f(x)=5−12x, 2≤x≤14, with six subintervals, points to be left endpoints.Подробнее

How to Find a Definite Integral using Riemann Sums and the Limit Definition: Quadratic ExampleПодробнее
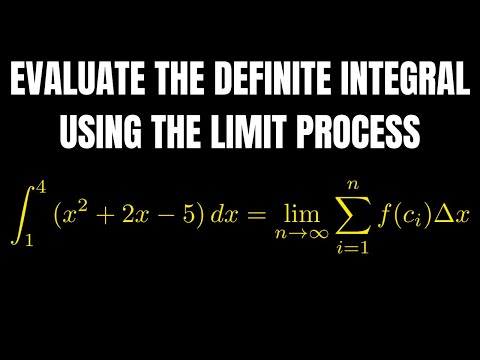
Riemann Sums - Midpoint, Left & Right Endpoints, Area, Definite Integral, Sigma Notation, CalculusПодробнее

Riemann Sum Evaluation of Definite Integral(Quadratic)Подробнее
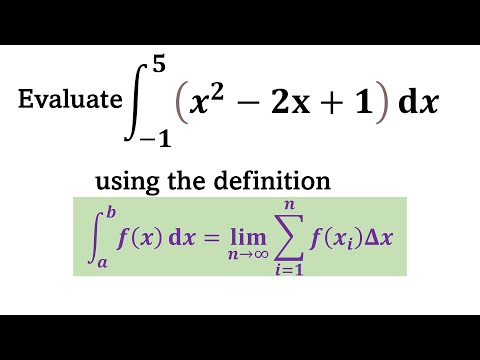
Evaluating a definite integral using a Riemann sum, part 2Подробнее

Right Riemann SumsПодробнее

Riemann sumПодробнее
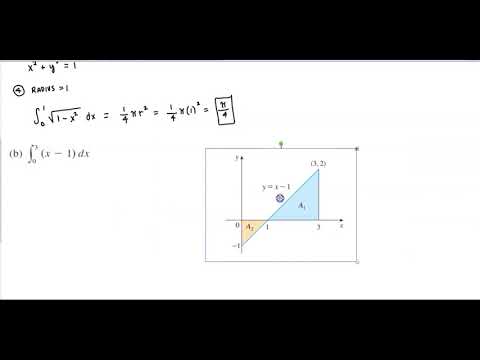
Math 1A 5.2 Example 4 Using geometry to evaluate integralsПодробнее
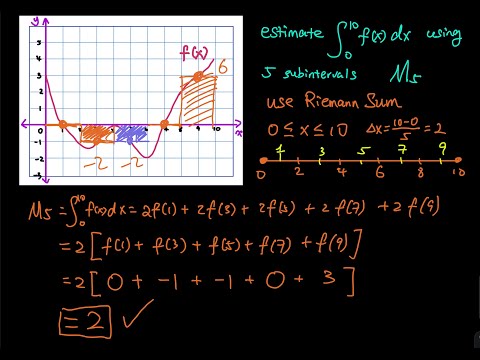
5.2 Part 6/8: Use Riemann Midpoint Sum & Graph to Evaluate Definite Integral | Integral CalculusПодробнее
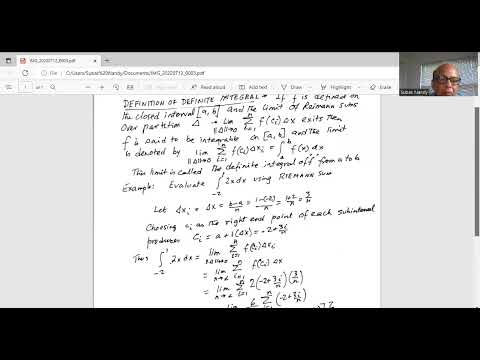
Math 1A 5.2 Example 2 Evaluating an integral as a limit of Riemann sums Part AПодробнее

Evaluate Definite Integral using Limit Definition with Riemann SumsПодробнее

Hammack's Calculus I, Lecture 41: Area and Riemann SumsПодробнее